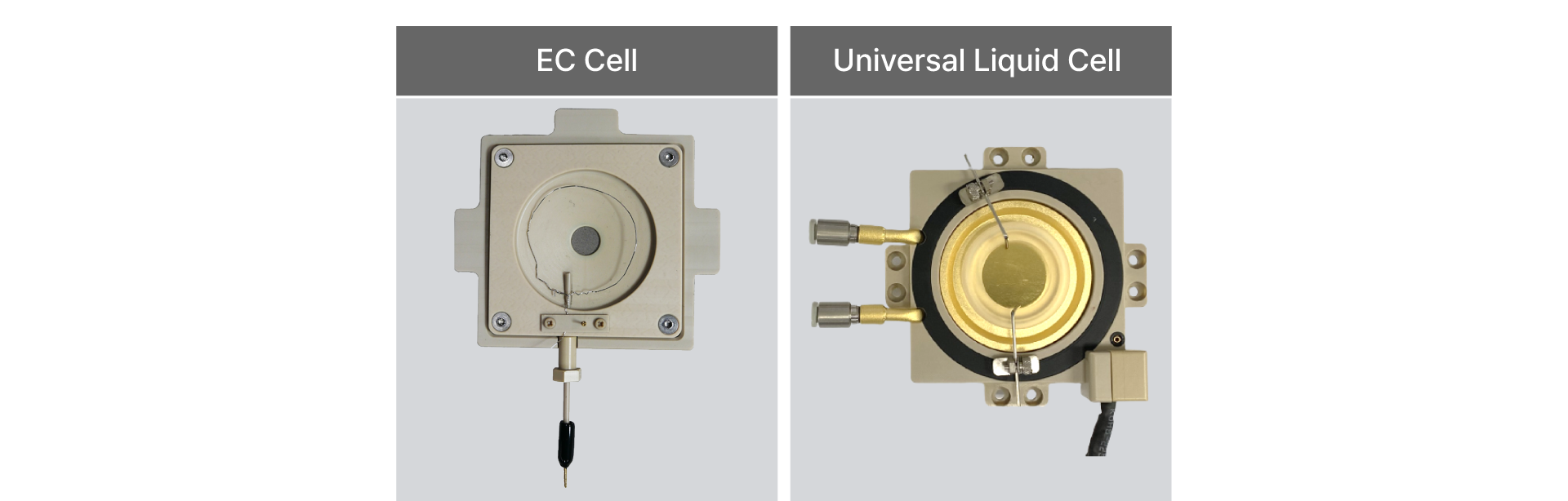
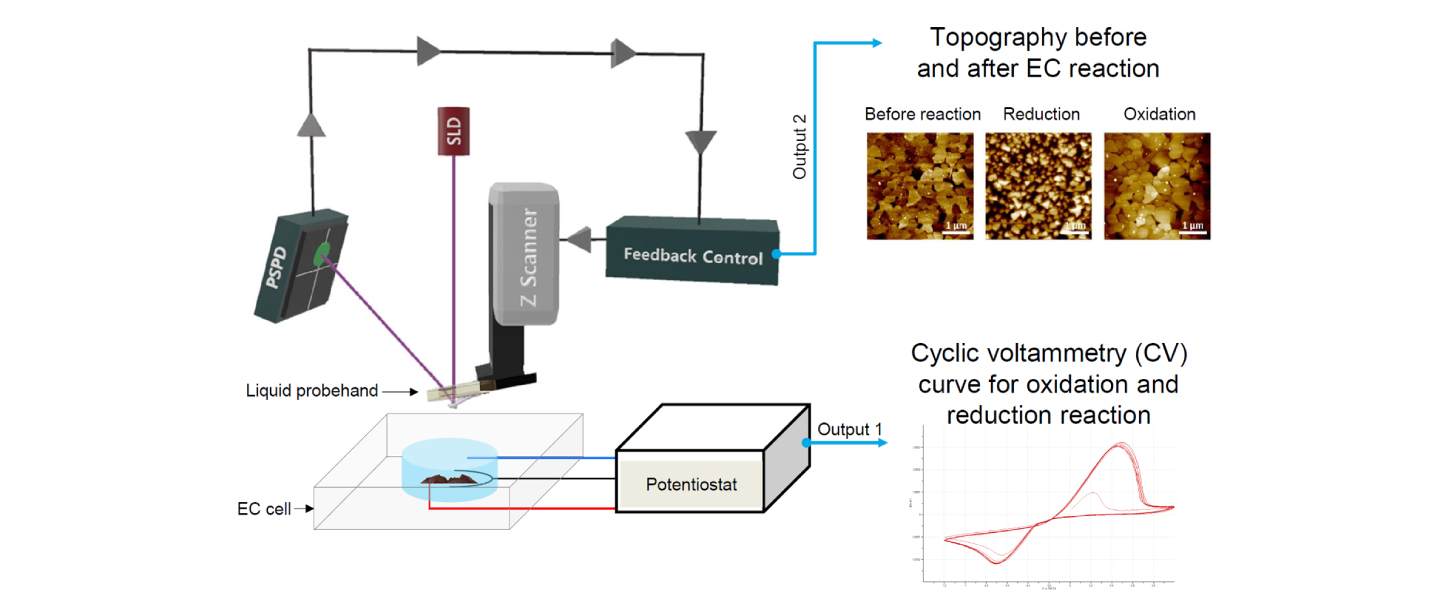
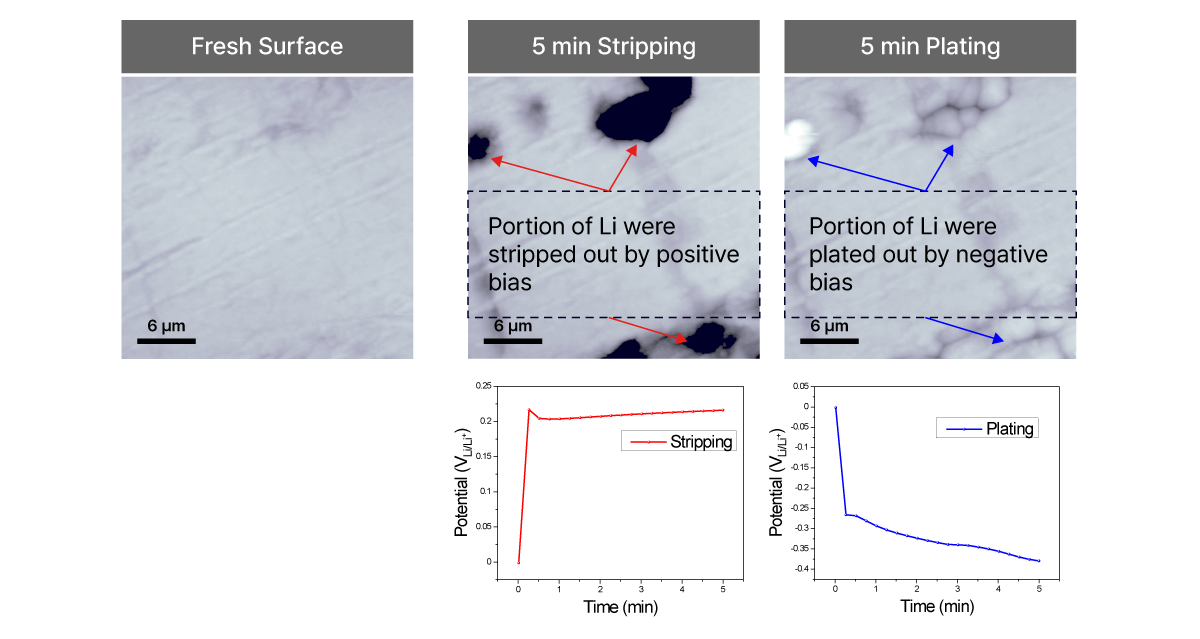
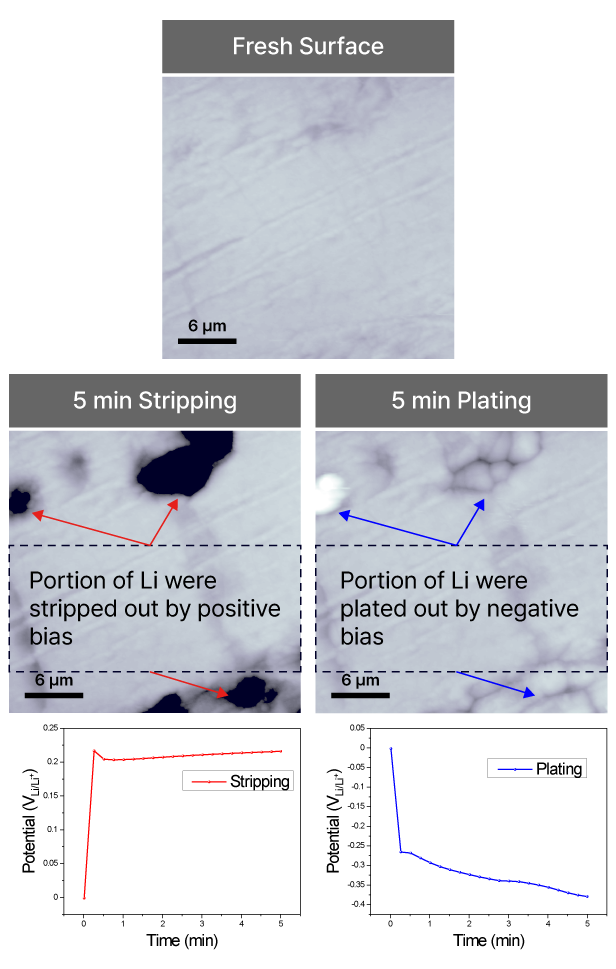
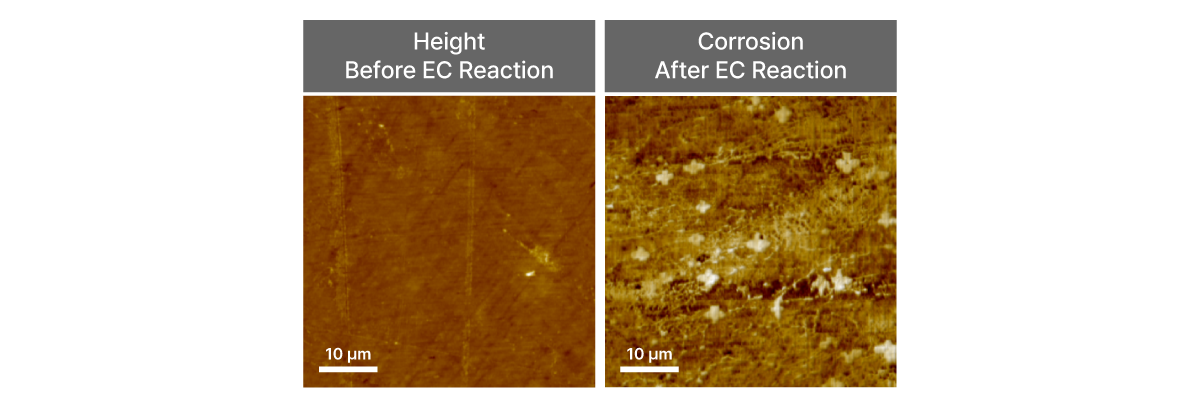
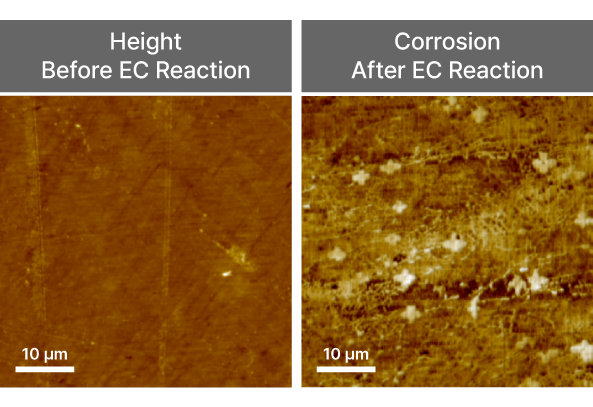
Electrochemical AFM
EC-AFM
In-situ imaging of electrochemical reactions in liquid environments